In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, Google now stands at a critical crossroads as regulatory pressures mount from the European Union. The tech giant, long criticized for its preferential treatment of its own services, may soon face significant repercussions for its actions, including fines that could soar to 10% of its global revenue. With the implementation of the Digital Markets Act (DMA), the EU aims to ensure fair competition and curb monopolistic practices. This impending legal challenge highlights the complexities of balancing user satisfaction, regulatory compliance, and corporate strategy in an era where transparency and fairness are paramount.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Issue | Google may face fines for prioritizing its own services over others. |
| Potential Fines | Fines could reach up to 10% of Google’s global revenue. |
| Regulatory Body | European Union (EU) regulators are investigating Google. |
| Background | Google has faced many legal challenges, especially under the Digital Markets Act (DMA). |
| Recent Changes | Google changed its Search results format in the EU but found users dissatisfied. |
| Test Outcome | The test did not increase clicks for third-party sites or hotel bookings. |
| Next Steps | Charges against Google are expected soon, though details are unclear. |
| Stakeholders | Users, regulators, and tech companies have competing interests in this issue. |
Understanding Google’s Challenges with the EU
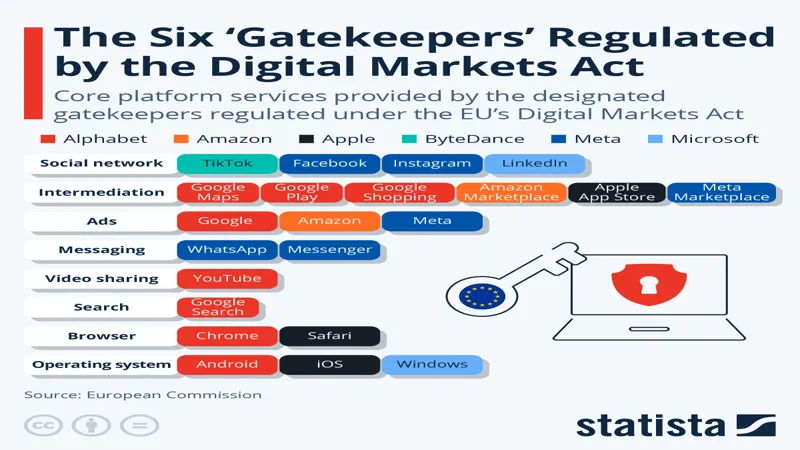
Google has been facing challenges from the European Union (EU) for quite some time. The EU has specific rules designed to make sure that big companies like Google don’t unfairly promote their own services over others. This is important because it helps smaller companies compete and gives users more choices. If Google continues to prioritize its services, it could face serious consequences, including hefty fines that could reach up to 10% of its global revenue.
These challenges are a part of the EU’s Digital Markets Act (DMA), which aims to create a fair digital market for everyone. The DMA has put pressure on Google to change how it operates in Europe. As the scrutiny increases, Google is being forced to think about how it displays its services and how it affects its competitors. This situation is crucial because it highlights the importance of following rules that promote fair competition.
The Impact of the Digital Markets Act
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) is designed to prevent big tech companies from taking advantage of their size and influence. This law is essential for ensuring that companies like Google cannot simply push their services to the top of search results, leaving out smaller competitors. By promoting fairness in the digital marketplace, the DMA helps create an environment where everyone has a chance to succeed, which is beneficial for consumers and smaller businesses alike.
As the EU implements the DMA, it’s crucial for Google to adapt its practices to comply with these regulations. Failure to follow the DMA can result in significant penalties, which could affect Google’s operations not just in Europe but globally. The DMA represents a shift in how digital markets are managed, and its impact will be watched closely by other countries and tech companies around the world.
Recent Changes in Google’s Search Results
Recently, Google attempted to change its search results in Europe by removing its hotel booking tools. This was a test to see if they could comply with the EU’s DMA. However, the results were not what Google hoped for. Users were unhappy with the new format, and it did not help third-party hotel websites get more clicks or bookings. This experiment showed that simply changing how search results are displayed is not enough to satisfy both users and regulators.
The failure of this test indicates that Google needs to rethink its approach to search results. Users expect to see relevant and useful information quickly, and removing tools they find helpful can lead to frustration. As Google navigates these challenges, it must find a balance between complying with regulations and providing a quality service that users love. This is a tricky situation, and Google’s next steps will be crucial.
The Potential Consequences of Non-Compliance
If Google is found to be in violation of the Digital Markets Act, the consequences could be significant. Fines could reach up to 10% of Google’s global revenue, which is a massive amount of money. This could affect how Google operates and could lead to changes in its business model. The threat of these fines is a strong motivator for Google to comply with the EU’s regulations and ensure fair competition.
Beyond financial penalties, non-compliance could also damage Google’s reputation. Users and businesses may lose trust in a company that does not follow the rules. This could lead to a loss of users and a decline in market share, especially in Europe where regulatory scrutiny is high. Therefore, it is in Google’s best interest to adapt its strategies and prioritize fair competition.
User Satisfaction and Market Competition
User satisfaction is key to the success of any service, including Google. When users feel that they are not getting the best results or choices in their search, they may turn to other options. This is why the EU is focusing on Google’s practices; they want to ensure that users can access a variety of services and not just Google’s offerings. A competitive market is good for everyone, as it encourages innovation and better services.
However, achieving user satisfaction while adhering to regulations can be challenging for Google. As they navigate the demands of the EU, they must also keep their users happy. This means that Google has to listen to feedback and make adjustments to their services. If they can successfully balance these demands, they may not only avoid fines but also strengthen their position in the market.
Looking Ahead: Google’s Strategy Changes
With the potential for fines and increased scrutiny from the EU, Google must rethink its strategies moving forward. This could mean making more space for third-party services in search results and ensuring that users see a variety of options. Adapting their approach is crucial to maintaining compliance with the Digital Markets Act while also keeping users satisfied.
In the coming months, it will be interesting to see how Google adjusts its practices. They may need to experiment with new formats that promote fair competition and better user experiences. By embracing change and prioritizing user needs alongside regulations, Google can work towards a successful future in the European market.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Google facing legal issues in the EU?
Google is under scrutiny for prioritizing its own services in Search results, which may violate the EU’s Digital Markets Act designed to ensure fair competition.
What is the Digital Markets Act (DMA)?
The DMA is a law in the EU aimed at promoting competition by preventing large tech companies from unfairly favoring their own services over others.
What could happen to Google if found guilty of violations?
If charged, Google could face fines of up to 10% of its global revenue for breaching anti-competitive rules.
What changes did Google try in its Search results?
Google attempted to simplify its Search results by removing hotel booking tools to comply with the DMA, but this led to user dissatisfaction.
How did users react to Google’s changes in Search?
Users were unhappy with the removal of booking tools, and third-party websites did not gain more clicks, resulting in fewer hotel bookings.
When might Google face charges for these issues?
Reports indicate that charges could be presented in the coming months, as the EU continues its investigation.
What does this mean for Google’s future in Europe?
The outcome of these charges could lead to significant changes in how Google operates in Europe, potentially improving competition.
Summary
Google is facing potential fines that could reach 10% of its global revenue for violating competition rules set by the European Union (EU). The EU is concerned that Google Search prioritizes its own services over others, like hotel bookings. Last year, Google tried to simplify its search results by temporarily removing its hotel booking tools, but this led to user dissatisfaction and fewer bookings overall. As a result, Google stopped the test. Now, the EU is preparing to charge Google for not complying with the Digital Markets Act, which aims to ensure fair competition online.